Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Managing inventory is a critical part of any business, and the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model helps strike a balance between ordering costs and holding costs.
Whether you run a small business or manage supply chain operations in a large enterprise, implementing EOQ can reduce waste, optimize cash flow, and improve operational efficiency.
This article will explain EOQ in simple terms, why it’s important, and how to apply it effectively in your business.
What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)?
EOQ is a formula that helps determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs. The goal is to order just enough inventory to meet demand without overstocking or ordering too frequently.
The EOQ formula is:
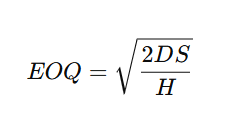
Where:
- D = Demand (units per year)
- S = Ordering cost per order
- H = Holding cost per unit per year
Using EOQ, businesses can avoid excess storage costs, stockouts, and inefficient order cycles.
Why is EOQ Important?
Implementing EOQ can help businesses in the following ways:
✅ Reduces Total Inventory Costs – Avoids unnecessary storage and reduces frequent order costs.
✅ Prevents Stockouts and Overstocking – Ensures you always have the right amount of inventory.
✅ Improves Cash Flow – Avoids tying up capital in excessive inventory.
✅ Streamlines Operations – Reduces the time spent managing inventory orders.
How to Implement EOQ in Your Business
Follow these step-by-step instructions to implement EOQ effectively.
Step 1: Gather Data
To use the EOQ formula, you need three key inputs:
- Annual Demand (D): Find out how many units of the product you sell in a year.
- Ordering Cost (S): Calculate the cost of placing each order (e.g., supplier fees, administrative costs).
- Holding Cost (H): Determine the cost of storing each unit per year (e.g., warehousing, insurance, depreciation).
- Example:
If a business sells 10,000 units annually, pays $50 per order, and has a holding cost of $2 per unit per year, the EOQ is:
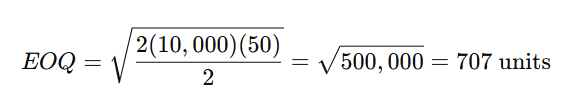
Step 2: Adjust Order Frequency
Once EOQ is calculated, determine how often to place orders using:
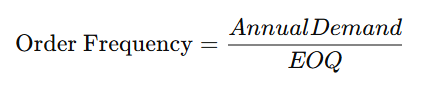
Example
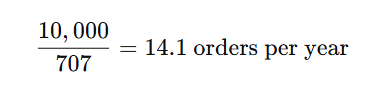
This means the business should place an order approximately every 3.7 weeks.
Step 3: Integrate EOQ into Your Ordering System
- Set up automatic reorder points in your inventory management software.
- Work with suppliers to adjust order batch sizes to match EOQ recommendations.
- Use EOQ insights to negotiate better pricing with suppliers for bulk orders.
Step 4: Monitor & Adjust EOQ Regularly
EOQ is not static—business conditions change, so update the calculations:
- If demand increases, EOQ may need to be adjusted upwards.
- If storage costs rise, smaller orders may be more cost-effective.
- If ordering costs decrease (e.g., cheaper shipping), EOQ may increase.
Common Challenges & How to Overcome Them
🚨 Fluctuating Demand: Use safety stock to handle unexpected demand spikes.
🚨 Supplier Constraints: Negotiate flexible order quantities with suppliers.
🚨 Cash Flow Issues: Align EOQ orders with revenue cycles to avoid cash flow strain.
Final Thoughts
EOQ is a powerful yet simple inventory management strategy that helps businesses save costs and improve efficiency. By understanding demand, ordering, and holding costs, you can make smarter purchasing decisions and avoid inventory pitfalls.
- Use the EOQ formula to find the optimal order quantity.
- Adjust order frequency based on EOQ calculations.
- Monitor & update EOQ as business conditions change.
Ready to dive even deeper into supply chain insights? Sign up now for our newsletter and get clear, actionable articles delivered straight to your inbox—no spam, just valuable tips to boost your forecasting and supply chain strategies. Join our community today!